Here are the notes I made for and took into the SENG4921 oral exam.
As an after thought, you can see I wasn't prepared for all the options but this is the best I could do in the time. Some of my arguments here may not be very valid, but this is my preparation as it stands, not a blog post into the questions (that's my excuse for being sloppy).
Question 1: free choice
- "Each student should prepare a topic of their own free choice concerned with some aspect of software, hardware, IT professional issues or ethics. This could be —but does not have to be— based on, or derived from, the discussions, seminars, debates, student run seminars and lectures given this semester. The question should be broad enough to not overlap with the other two questions. At the examination the student will be asked to present his/her topic and discussion. If the free choice question deals directly with one of the Seminar or Lecture questions, then this will generally eliminate that question if one of the randomly chosen 3 for question 2 or 3. Note carefully that the elimination occurs after the random choice, not before."
After a little thought I think I will focus on DRM in this question. I think this is a good choice because,
- Its not covered in the other seminar and lecture questions,
- I know enough about the topic to be able to talk about it,
- There are actually some valid ethical questions that can be raised and debated here,
- ...
So the deal is I only have 5 minutes to talk about the professional issues and ethics surrounding DRM. I need to identify the issues involved, analyse the professional and/or ethical consequences and present the outcome. I will need to be careful that I address the right things as I only have 5 minutes.
The examiners will be looking for:There are no correct answers, but a good answer will give a clear indication of consequences and issues.
- clear identification of the issues;
- analysis of the professional and/or ethical consequences;
- careful presentation of the outcomes.
Identification of Issues
DRM is digital rights management. DRM technologies attempt to control use of digital media by preventing access, copying or conversion to other formats by end users.
- DRM is used to bypass existing copyright laws and create your own. Content protected by DRM uses software or hardware measures to prevent unauthorised use of such content. An example is protected music purchased from the iTunes music store. The music is usually encoded using AAC, however on top of this it is encrypted. In simple terms you can only play this music on Apple approved devices. So you cannot play that music on a sony MP3 player, you cannot convert the music to MP3, you cannot play the music on another player on Linux, and lastly if Apple goes bust and decides not to free your music you will never be able to play the music you bought.
- How different is this to selling music using patented encoding techniques. No one else is allowed to make a player except you.
- I mentioned this bypasses existing copyright laws. An example of this is say you want to use a segment of the content you bought which is protected by DRM but the use of the segment is permitted under copyright laws. Regardless of the law you can't use the material either because you can't crack the DRM or even if you can, the process of doing so is illegal.
- Also most DRM systems are not set to expire when they are supposed to fall into the public domain. Thus the work may be public domain but no one can access it as its encrypted with some DRM mechanism and no keys no longer available. This undermines the concept of the public domain.
Lastly DRM systems do not work, as most have been cracked. Once the DRM has been cracked by one person (who may be an expert) then can distribute this clean version to all over say BitTorrent. DVD's CSS was cracked,
From personal experience a while ago I downloaded an e-book (actually a standards document) from the UNSW library/publisher of the standard. It was a PDF document and they told me that it would expire after a week or so. It turns out that it used some JavaScript hide the text when the system date was at whatever was a week after the PDF was downloaded (so the web server was creating the PDF on the fly putting the expiry date and the download details into the PDF). This could be easily bypassed by disabling JavaScript, using a free PDF reader that does not support JavaSript, and so on. Furthermore you could easily use some software to extract the content of the PDF and resave it without the DRM. (Will I go to jail if I ever vist the US because of the DMCA?? Or even from Australian laws?)
Professional and/or ethical consequences
Ken noted in his introduction article that "In this course, we will be particularly concerned with developing your capacity to reason about the possible outcomes." Hence I will try to focus on the affects/consequences of DRM. Taking a consequential approach to ethical thinking requires one to consider the possible consequences. So some consequences of DRM that should be addressed when taking a ethical approach to DRM are,
- Legitimate users soon find out that they can only use the products they thought they bought in situations that are approved. eg. you find out that your iTunes music won't play on Linux.
- Consumers become locked in to one vendor. eg. they may have purchased $100 worth of music, but they find they must buy an Apple MP3 player to use it and cannot shop around. Companies can use this advantage to raise the prices of their products to above market value.
- DRM systems that require a 'call back' over the internet to some key server won't work if the company goes bust. Hence if the company goes, so does all your music.
- Many consumers will be driven to consume pirated material as its generally DRM free so less hassles.
- The public may turn against corporations as a whole, due to those that have abused their honesty and good will. People may loose trust in companies and no longer purchase any material and just obtain pirated materials instead.
- Consumers/public may feel coned and abused.
These are all possible outcomes, yet they may not all be an ethical concern. This depends on your individual ethical principles. For me if DRM leads people to move to pirated material rather than paying the owner, then this under my ethical principles this is not a concern. This is strictly a business move and the consumer will not be harmed by doing this. If the company doesn't want people to pirate the matrial instead of buying it then they can simply remove their DRM and sell it DRM free.
But from a utilitarian perspective, DRM does little to stop the original creator receiving remuneration (if anything it may result in less remuneration), instead it causes great unhappiness. In this respect it is unethical.
As Cohen outlined professions come with these extra "professional" responsibilities. Including "public interest is paramount", public trust, but also client's interests. Most (if not all) DRM systems are not in the public's interest. They are riddled with problems and do very little to stop piracy. They turn honest customers into outlaws. The key thing that consumers need to be aware of is they are not purchasing products from the iTunes store rather they are purchasing a licence to use the music in a restricted set of conditions.
Question 2: Seminar Questions
1. "Engineering"
I think Wikipedia's summary of Engineering describes what is generally understood by the term 'Engineering'.
Engineering is the application of scientific and technical knowledge to solve human problems. Engineers use imagination, judgement, reasoning and experience to apply science, technology, mathematics, and practical experience. The result is the design, production, and operation of useful objects or processes.
Of course as a profession it comes with all the things that make it a professions such as responsibility to the public, client's interest, public trust, an so on.
Software and Computer Engineering can claim to be engineering professions as they meet this description of Engineering that I just quoted. Software and Computer Engineers apply scientific (mostly mathematical, or even Computer Science if you want) and technical knowledge to solve problems. They use experience and so no to apply this to the task at hand. They also do a lot of design work and the actual production of the software/hardware.
Computer programming vs. Software Engineering vs. Software Development
As a job title. Sure your official job title may be "Computer Programmer" or you may graduate with a "Computer Science" degree. That doesn't mean you never do any "engineering".
====
My opinion of what is generally understood by "Engineering" as a profession is (to quote Wikipedia here), "Engineering is the application of scientific and technical knowledge to solve human problems. Engineers use imagination, judgement, reasoning and experience to apply science, technology, mathematics, and practical experience. The result is the design, production, and operation of useful objects or processes." And of course as a profession it comes with all the things that make it a professions such as responsibility to the public, client's interest, public trust, an so on.
======
2/3. ACM Code of Ethics/Therac 25
- The ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct has the general ethical principles which ACM members must abide to. It also has the code of conduct part called 'more specific professional responsibilities' tell you what you should do in particular (but still general) situations.
- Section 1 Ethical Principles
- Contribute to society and human well-being.
- Avoid harm to others
- Be honest and trustworthy (was Cindy honest to her superiors about the tests?)
- Be fair and take action not to discriminate
- respect privacy
- honour confidentiality
- Section 2 Specific Prof Responsibilities
- professional competence
- Give comprehensive and thorough evaluations of computer systems and their impacts, including analysis of possible risks.
- "computing professionals must minimise malfunctions by following generally accepted standards for system design and testing."
- Access computing and communication resources only when authorised to do so.
- Section 1 Ethical Principles
- Killer Robot
- Randy Samuels
- Cindy
- The Therac 25 accidence were exactly that, they were accidents.
- The people involved were involved appear to have acted as per the ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct.
- Sure they could have done things better. Improved processes, done more checks, get it independently tested, acted on patient complaints.
- Really?
4. Technical Issues with the Therac 25 Case
- Therac 25 was a machine for treating cancer
- Had no mechanical locks like previous models
- Reused software designed for older models
- relied more on software than hardware (did they take this into account when designing the software?)
- investigations only began after several accidents
- causes
- software not independently tested
- user manual did not explain certain errors
At the end of the day (as with many famous disasters) there were many times where if something was done better the problem may not have occured.
6. Killer Robot
- Cindy Yardley - Faked software tests to save her co-workers jobs.
- Knowingly let the product ship with flaws.
- Thought it would be okay, but be open and let the people charge decide that.
- --
- "Give comprehensive and thorough evaluations of computer systems and their impacts, including analysis of possible risks."
Randy Samuels - Wrote the code that cause the robot to malfunction.
8. Intellectual Property
- Do people still use Windows 3.1? Can you still buy it? Its economic value now is probably close to zero. Why is it still protected then? If copyright was designed to encourage new works then surly by freeing up old works such as Windows 3.1 gives Microsoft an incentive to make something new and better.
- Creativity always builds on the past, yet we cannot make derivative works because of copyright laws.
- Data is now protected. And any situations that are not clear may take $$$'s to be decided by the courts. Need better statutory law and modern.
- Scientific knowledge. Most is public knowledge allows ideas to be examined and challenged and improved. Increasingly this is becoming private with genetic engineering.
- What if the internet was patented. Consider a) they essentially stoped all developments or b) make $$$'s from it when obviously we needn't' that cost for it to work. Inner workings were shared without the need for patents.
- Think much open source software.
From an ethical analysis,
- some 3rd world people have to pay to use seeds that have been freely available to them for centuries (this is very anti-utilitarian).
Affects Computer Scientists and Software Engineers.
- GIF Patent
- eg. iPhone developer not allowed to use CityRail data
- When copyright laws are used in this way to stop the spread of information then it counters many ethical principles, openness, fairness, sharing of information, helping someone when doing so will do no harm to you
From an economic view,
- Making a copy does no harm (negative benefit) to the person you copy from. Compared to stealing which takes it away from them. At most you may be removing potential sales.
9. Datavallience
Two types of dataveillance.
- Personal Surveillance (singled out)
- Mass Surveillance
Three examples,
- Government monitoring of internet traffic. (spying)
- Data collection of online services. (eg. facebook data gathering)
- Employer monitoring employee email.
Professionals have a responsibility to act in the public's interest (as well as the clients interest). They also have codes of ethics to adhear to. Many ethical principles would lead to the conclusion that the people who are having their information monitored should be notified of this. To act in the public interest, the public needs to know when they are being monitored. This gives them the choice, to either use encryption, stop using the service, or something else. However professionals should make an exception to this rule when the matter is of national security or something other when it can be justified that not notifying is acting in the publics interest. This is what ethics is all about. Dealing with these exceptions to the rule.
- What is dataveillance?
- Is it immoral to collect data about other people?
- What personal data is currently being collected?
- What new opportunities are there to collect even more personal data?
- How can dataveillance be regulated?
- What advice would you give to non-specialists about safeguarding personal information?
It depends on the situation. The ethical approach I subscribe to is that the person who is having data collected on them, should be made aware of what is being collected, and that it is being collected.
Question 3: Lecture Questions
- give an overview of the lecture;
- describe the important professional and/or ethical ideas raised in the lecture, especially those that impact on Software/Computer Engineers and Computer Scientists;
- Important answer any specific questions attached below to the lecture.
1. Theoretical Underpinnings of Ethics
"Essentially, you are being asked to demonstrate how different ethical principles could be used to produce different outcomes. The important part of your answer will be the identification of the different principles and how your reasoning would proceed from those principles."
Overview
- Humans around the world all tend to have the same ethical concepts. Integrity, fairness, honesty, openness...
- Relativism is doing what the culture is doing just because everyone else is doing it. This does not make it right. People are too quick to play this relative card.
- When we talk about ethics we mean prescriptive ethics. This is what you should or ought to do, compared to descriptive ethic which is what people do do.
- Ethical can be contrasted to,
- prudential (self interest)
- political (vote of opinion)
- preference (want rather than should)
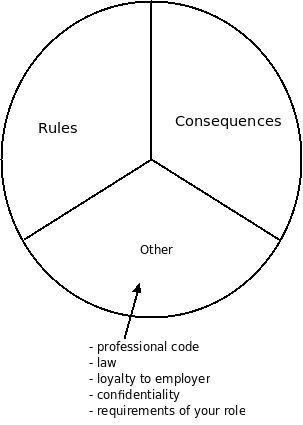
- Rule, Consequences, Professional Code, law, loyalty to employer, confidentiality all factor into ethics. Rules and consequences fall into private (individual) morality, the rest is public morality which matters when you occupy a role.
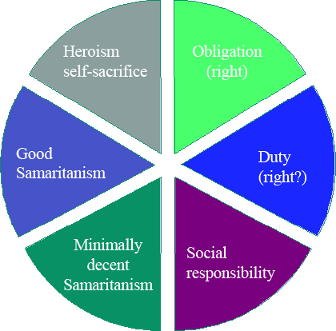
- There are different levels of morality. In order,
- Obligation (signed agreement)
- Duty (eg. its your duty to treat every human with respect)
- Social Responsibility (duty without specific target)
- Minimally Decent Samaritan (go the extra mile to help them)
- Good Samaritan (someone asks you the time, you tell them)
- Heroism/Self-Sacrifice (wistleblowing)
And now on to the part relevant the the question at hand,
- Two different ethical principles are consequential (teleological) and non-consequential (deontological).
- Under the non-consequential view,
- to determine if an act is right or wrong it in fact has nothing to do with the consequences of the act. Instead it has to do with other things such as rights, duties, contracts, fairness, etc.
- Kant's idea was that good will is what makes an act right, where good will is recognising your duty and then being able to make yourself do it (eg. you crash into a parked car you realise it is your duty to leave your details and then your able to make yourself to do that, even if you don’t want to do it).
- Under the consequential view,
- Acts are right based on their consequences.
- We have,
- Utilitarianism - “Acts are right insofar they produce happiness and they are wrong insofar as they don’t produce happiness.”
- Nationalism - “Acts are right if they are in the best interest of the nation as a whole.”
- Epistemism - “Acts are right insofar as they advance our knowledge, and they are wrong if they don’t do that.”
- Example. A dangerous criminal who commited murder and who is very likely to do it again falls into a dangerous situation (eg. is downing). It may very well be your social obligation to throw them an inflatable tube. That would be the fair thing to do, and it would be your social responsibility. However that would not be considering the consequences. Taking a consequential approach, the consequences of saving this one person may cause great unhappiness (and great risk of harm) for the people who the drowning person has threatened to kill. The ethical thing here may be to let him drown in order to save the lives of many others. But again this all depends on your ethical principles.
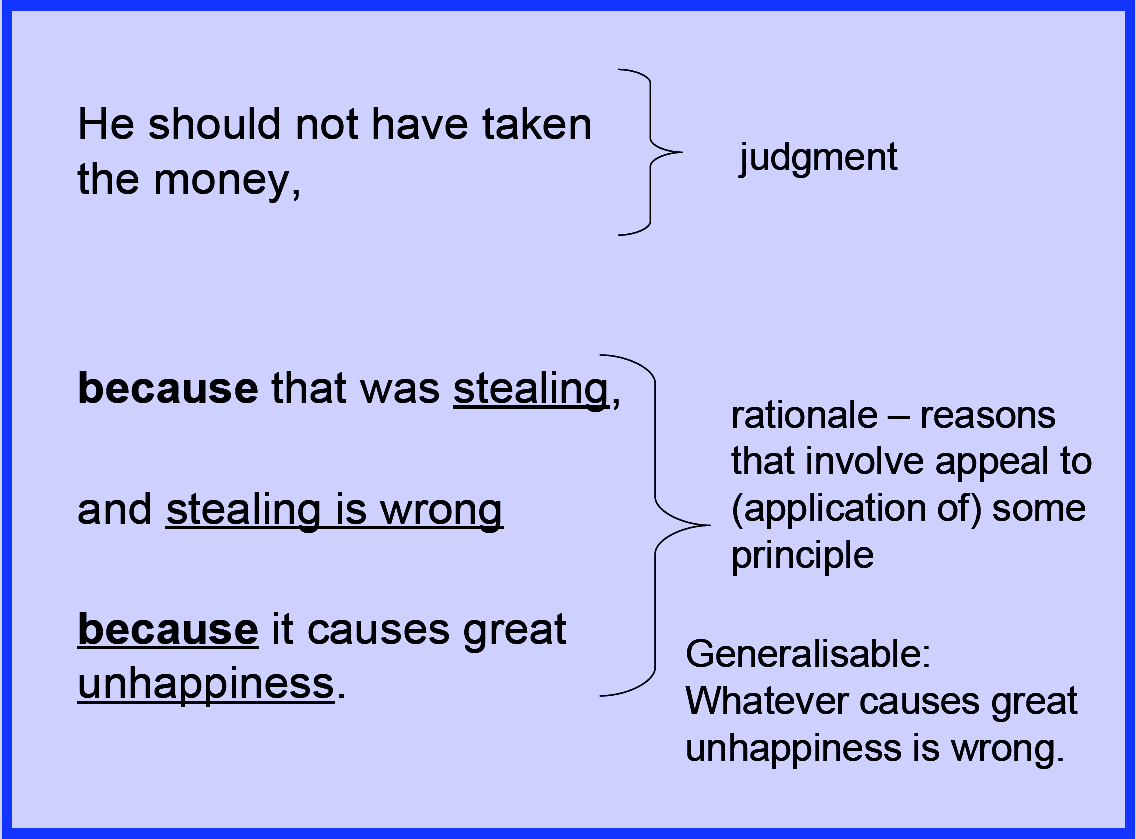
To make a moral judgement you need to make a judgement, have some justification for that judgement, and also have some principle that lead you to believe that that justification was right. (judgement > justification > principle) If you don’t have this, you don’t have a moral judgement.
2. Professionalism and Ethical Responsibilities
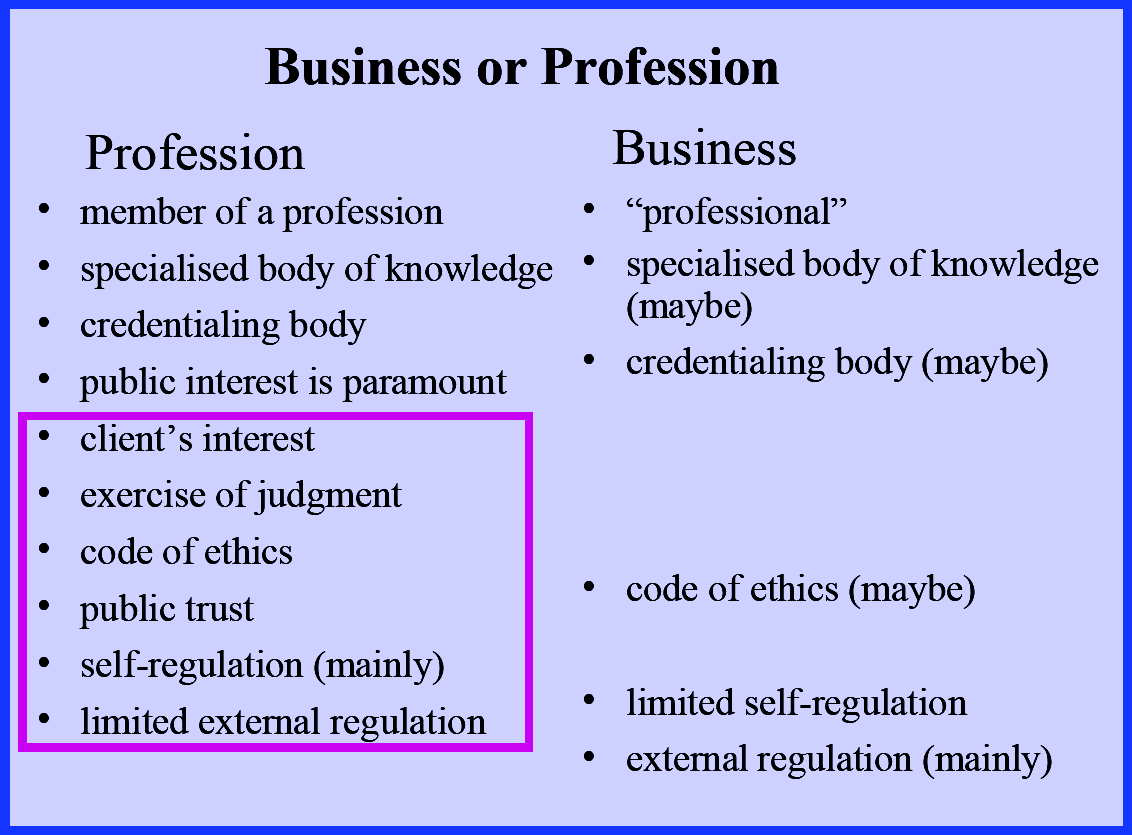
- The key thing that distinguishes professionals or a 'profession' is professionals have these extra public ethical responsibilities.
- act in client's interest
- exercise of judgement
- code of ethics
- public trust
- act in public interest
- This is what separates a profession from a business (or a professional from a businessman). These extra things are their duty. Professionals have an obligation to oblige to these things. cf. businessmen are not ethically obliged to act in the public's interest.
- They have a duty to survey the whole landscape and do what is best.
- Conflict of interest. You can’t be a profession if you have some extra incentive (eg. being paid to do something against the client and public’s interest). “A person’s having a conflict of interest is not the same thing as a person’s being affected by a conflict of interest.” People who say they don’t have a conflict of interest just because they are not affected by (or more specifically their judgement is not affected by) a conflict of interest doesn’t mean they don’t have a conflict of interest.
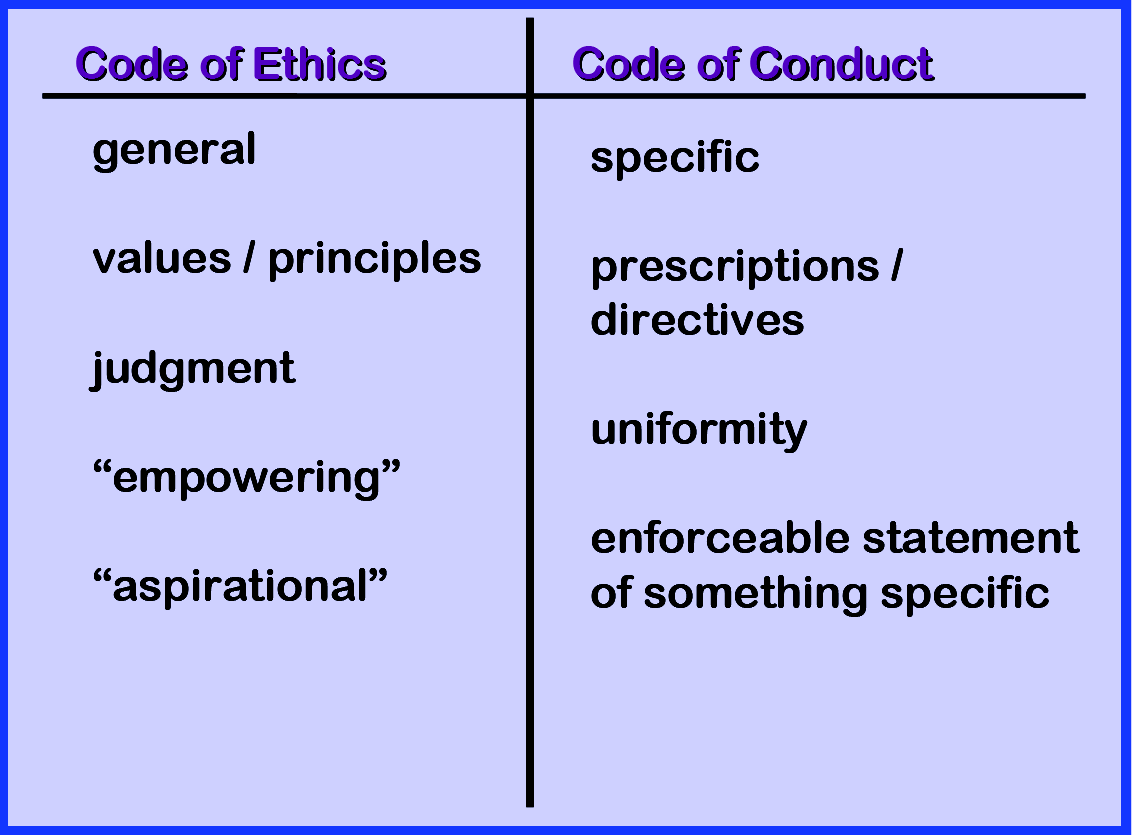
- Codes of Ethics and Codes of Conduct. Codes of Ethics have values/principles. (eg. honesty, openness)
- Any principle/value will require judgement.
- You make a judgement on the principle/value, and in this respect Code’s of Ethics are empowering. (eg. guy here to kill someone, honesty does not require you to tell him where to find the person).
- Code’s of Conduct are different. They are not for introducing new values. They are there to remove judgement. They tell you exactly what to do in specific situations. eg. Bribes. They may say that you cannot accept any gift you receive over a given about. They take the heat off.
Other things of interest,
- “At work, you don’t leave your private, personal values at the door!” “Your ethical values must be there.”
- The answer to “Who’s to judge” is always “You, as an individual.” (from whatever perspective whether it be legal, ethical…)
3. Open source from an Economical Approach
- Software is a Collective Consumption Good. Consumption by one consumer does not reduce consumption by any other. Also “non rivalrous”.
- Software is Nonexcludable = difficult to exclude others from use
- Goods which are both lead to incentive to free ride, Results in “Market Failure”
- Argument is that, therefore software will not be produced unless there are special rights restricting the exploitation of software.
- According to this, these are not possible
- Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP, Email, Internet protocols
Closed source (Sales Force): For every $1 spent on software development, $10 is spent on marketing Open Source (SugarCRM): for every $4 spent on development, $1 is spent on marketing
6. Freehills Talk/Software Patents
Quick Summary
- Patents are a business tool.
- Monopoly vs. Secrecy
- Patentability (any prior art)
Ethical issues for Software Engineers/Computer Scientists
- Patents cost $$$, and take time. Is this worth it.
- What if the internet was patented. Consider a) they essentially stoped all developments or b) make $$$'s from it when obviously we needn't' that cost for it to work. Inner workings were shared without the need for patents.
- Think much open source software.
This comes down to your ethical principles. My ethical principle resolve around helping others, advancing knowledge, and working together for maximum benefit. So under my ethics software patents are unethical because they hinder the progress and development of (in the case of software patents), software. For example, someone patents the GIF encoding scheme, this can be used to lock out people from using this method. It also locks the scheme up so in the theoretical case where someone patents X, which lasts for 20 years. Person B invents X two years later but cannot use or distribute that invention because of the patent.
If you don't want others exploiting or using or building on your invention then don't share the details with anyone.
We are forgetting that many people (think Linux) don't need the incentive of a patent to invent things or make them useful to the public. Patents hinder the publics access to certain processes.
If everyone was free to take others hard work and put it to good use, and build upon it and share that then progress would move faster than ever before.
But this is just my view of the matter. I do grant that I have this view because for me, progress (in terms of new and better software, etc) comes by people working on their own will because they want to for the fun of it (an example open source software, much of it was done with little commercial incentive). No money is wasted on lawyers who make no progress to the field. Instead everyone can work on pushing progress forward.
The ethics is solid. In fact patents were originally designed very ethically. Look at the consequential utilitarianism approach.
But things have changed. Software patents have not helped with this.
- Look at Mathematics > no patents. Much progress. Much work is based on previous work. (imagine if some theorems were 'protected' for 20 years and you could not discover any theorems that used that original theorem in its conception or proof)
- Have Software Patents really done what the patent was meant to do? No. The consequences of having patents was originally that the inner workings and methods of creation of an invention were published to the public for their good. But patents don't have source code
Back to patents.
7. Law
- Statutory Law. Parliament.
- Common Law Courts.
- 4 jurisdictions
- criminal
- civil (tort and contract)
- administrative law
- equity
- litigation is the process or a lawsuit
- burden is on the plaintiff (the one brining the action)
- can be $$$
- putative damages (in contrast to compensatory damages) are not to compensate rather to reform or deter the defendant/others from doing the act/repeating it.
- Windows and the iPhone are licensed. They come with a license agreement.
Well as an ethical professional engineer you have an obligation/duty to act in the client's and the public's interest. As such you should notify the company of the situation and let them make a decision based on that. This is acting in the clients interest. Even with out this certain ethical principles such as openness may require you to notify the other party
Contrasted to an ordinary businessman who has no duty (thought they ought to do at least what is minimally decent) to act in the publics interest.
Different Standards when choosing to obey a law or not. Illegal? Litigation Risk? 'Professional' Standard(will your peers reject you)? Ethics(will your friends and children reject you)?
9. Internet Censorship
Overview
Professional/Ethical Ideas / Social/Technical
- There is a lot to talk about this topic.
- Censorship.
- Should there be any censorship?
- Internet Content Classification.
- Should there be a gov department which pro-actively classifies all the sites on the web? eg. DET. From a technical view, the web is huge and dynamic. There is no way that one gov department can keep up with this. eg. 20 hours of video is uploaded to youtube every minute.
- Should classification work on a complaint system? People who oppose could just flood it.
- Two other options.
- Community classification (rely on good faith, ie allow people to label certain URL's as adult only... if you get enough people to 'vote' then the results should be good).
- Host classification. Make laws that require the content host to label any content they make available online.
- From an ethical standpoint, your ethical values/principles (mine do) may require you to at least make a reasonable attempt to provide users with classification information.
- Transparency is one of the criticisms. If decisions are made behind a closed door then this leads to abuse (eg. blocking political speech). Need public scrutiny and pressure to keep it in line. Taking a non-consequential ethical approach we need transparency for this scheme to meet the ethical principles of openness, fairness, honesty, integrity and so on. From a consequential approach, much research would need to be undertaken to consider the consequences, and this is something the governments reports should address. With the research in hand and from a utilitarian approach would censorship with no transparency produce the most happiness, or from an epistemic approach would this case of censorship without transparency really advance knowledge more than no censorship or censorship with transparency?
- This is real and at the end of the day it is computer scientists or software engineers that will implement any censorship. As such in the end it will come to these people to make an ethical decision on whether what they are doing is ethically right under their principles.
A social issue is over-legislating. eg. . For example certain materials (which probably includes child pornography) is illegal to view, so if you happen to accidentally find this material on the internet and you want to report it to the police so they can track down the perpetrator, you are in a conundrum. If you tell the police about it, then you must have viewed the material yourself which is illegal so you may face criminal charges, hence you cannot report it.
Another social issue. Is it just illegal content? Should the government be deciding what to view or not?
Technical Issue. What about things like VPN's, tor...? The internet is huge and dynamic? What about a tag system.