I try my best to be accurate, but I would not be surprised if I have made some errors here. Also this post is still a work in progress and I'll be making changes.
Week 1 & 2
Historical Origins of The Australian Legal System
- Common Law Legal System
- Australia has a "Common Law Legal System". The main feature of this that separates it from other Western legal systems is the degree that it relies on precedent (through the doctrine of precedent). Under this system laws either come from Parliament, called legislation, or Courts, called case law or common law.
- I've come to realise that its not enough to just follow just the legislation as cases can provide extra details and insights into the legality of a matter. Furthermore you can rely on these precedents in court (although it seems they can go back on their decisions and make new precedents to override old ones, as seen with [2009] HCA 14.).
-
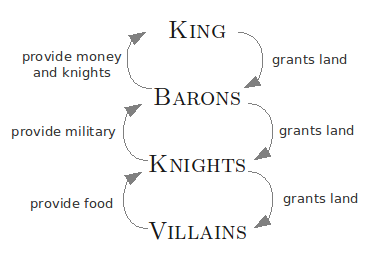
Institution Laws People parliament statute law members of parliament courts common law judges (most courts)/magistrates (in the local court) - Barristers are the ones in court arguing a case, eg. in litigation. Solicitors are the people you usually go to see first. They can arrange a barrister, draft wills, give legal advice, etc.
- Norman Period
- Australian Law stems from English law. English Law started out in the Norman Period.
- Feudalism
- Trials by Ordeal and Trials by Battle.
- Relied on "divine intervention" to determine the verdict.
- The Writ System (court orders...)
- Lead to Equity.
- Equity -> eg. forced to comply with the contract.
- Constitutionalism -> Can be thought of as 'guidelines for government'
- Magna Carta
- Just an old document. But an important clause was that no one could be detained without being charged, and right to trial.
- allowing appeal against unlawful imprisonment.
- Includes,
- A right that a person can seek relief from the unlawful detention of him or herself, or of another person.
- Westminster (Parliament)
- Monarchy <-> Republic
- House of Lords/House of Commons (Upper House/Lower House)
- Parliament
- Legislative Arm -> Creation of laws
- Executive Arm -> Administration of laws
- The Bill of Rights 1689
- Non-Partisan - Not affiliated with a political party
- Security of Tenure of Judges - Protects from external pressure. ie. contractual right not to be sacked without just cause.
- Trial by Jury
- Originally (ages ago in England) the jury were locals, now they are impartial (and so are the judges) which means that they have no prior knowledge of the case.
- Saxton's introduced compensation into the law
Week 3
Rule of Law
The rule of law had origins in the Magna Carta but its not what we now consider "the rule of law".
The key theme of the Rule of Law is everyone is subject to the law.
Eight Ways to Make Law Fail (based on the allegory concerning Rex):
- Failure to publicise law
- Obscure law
- Retroactive law
- Contradictions in the law
- Unable to comply with the law
- Unstable daily amendments to the law
- Differences between rules/laws as announced and their administration
However at least some of these (if not all) are not law themselves. They are not in the constitution so there is nothing stopping a government from creating say retrospective law.
Law, Land & Society Before 1788
Terra Nullius is a term used to describe be land belonging to no one. The British belied Australia to be Terra Nullius as they did not see the land as having an established legal system.
Week 4
Types of Legal Systems
- Common Law
- Adversarial System (this is the type of procedure practised in common law courts)
- "relies on the skill of each advocate representing his or her party's positions and involves an impartial person, usually a jury, trying to determine the truth of the case." (Wikipedia.org, Adversarial System)
- Mostly done orally in the court room.
- Adversarial System (this is the type of procedure practised in common law courts)
- Civil Law
- "The Code"
- No precedence (so there is no case law)
- Inquisitive System (this is the type of procedure practised in civil law courts)
- "has a judge (or a group of judges who work together) whose task is to investigate the case" (Wikipedia.org, Inquisitive System)
- Mostly done through written submissions to the judge.
- Judge actively steers routes of evidence investigation (compared with a common law system where the lawyers do this).
- No jury (mostly).
- Communist Law
- Religious Law
- Customary Law
- eg. Aboriginal customary law
- Never written down
These legal systems "supposedly" all have the same aim.
Separation of Powers
Kept separate to balance power of any one:
- Legislative Arm (Parliament)
- Amends/Creates Laws
- Executive Arm
- Administrate Laws/Initiating Laws/Enforce laws
- Government Departments, Governor General, Police...
- Judicial Arm
- Courts/Judges (High Court...)
- Interpret laws
Jurisdiction is the power of a court to exercise judgement.
Three different types of jurisdiction,
- State vs. Federal
- Original vs. Appeal
- Civil vs. Criminal
Week 5
Federation and Laws Made By Parliament
- Australia Act 1986 (ie. federation) (according to the constitution) stipulates the number of senators and the distribution among the states.
- It was not until the UK passed their statues did Australia become legally a federation.
- Senate (Upper House) -> Scrutinise Bills
- House of Reps (Lower House) -> Draft/Introduce Bills
To get voted into the senate you need 1/6 + 1 of the votes. Once you reach this quota extra votes that would be used on you are distributed to the voters other preferences. Senators are only up for election every two elections (usually).
- Senate -> Representative of the State
- Reps -> Representative of the Country (Although its a little more detailed as they are really representative of the electorate. Because of this you can have a party with 49% of the votes but still get no members into the house of reps.)
We generally get lots of independents in the senate because people rarely vote 1. Labor 2. Liberal. If someone supports party A where B is A's greatest competitor, most people will usually not vote for their opposition as 2, so they sometimes put some independents (remember once the quote is met, surplus votes are redistributed (either as the voter order their preferences, or if not chosen by the voter, how the party chooses)).
- With regards to politicians voting on bills, a Conscious Vote is crossing the partly line (or whatever the party decided on how they would vote) vs. a Party Vote where you (the politician) vote as your party does regardless on what you think.
Preferential Voting ensures a strong 2 party system.
Passing a Law: (Repeated for each house)
- 1st Reading
- 2nd Reading - Purpose of the bill (Sometimes used by lawyers to interpret the law).
- 3rd Reading
The Australian Constitution stipulates which matters the Commonwealth have power to make laws over and which the states have power.
Week 6
Laws Made By Courts & Precedent
An indictable offence is one where you can go to prison over it.
A case begins in the local court with committal proceedings, except for the more serious cases which begin in the supreme court. But there are some exceptions, for example certain constitutional cases will go straight to the High Court.
The different courts are listed http://www.austlii.edu.au/databases.html, although the list is not complete as you also have local courts in most states.
Local court -> District Court -> Supreme Court -> High Court.
[caption id="attachment_756" align="aligncenter" width="450" caption="Hierarchy of the Australian Courts"]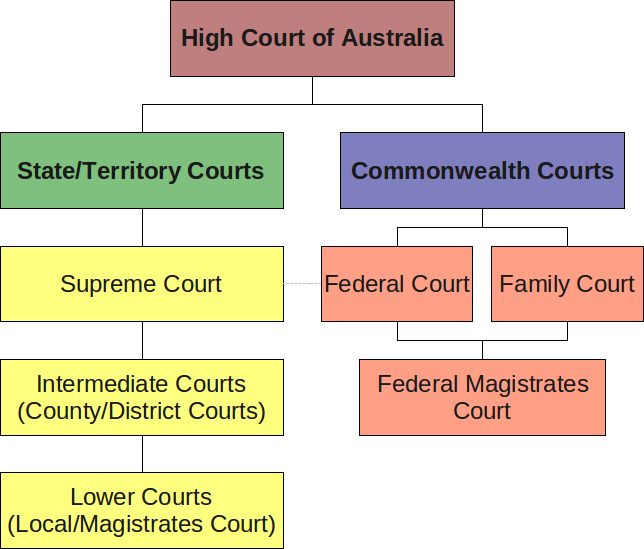 [/caption]
[/caption]
- If you don't like the decision make by one court you can appeal to a higher one.
- For a matter to be heard in court there must be "reasonable prospects of success".
- Civil matters claiming over $750 go straight to the supreme court.
In a criminal case beyond a reasonable doubt must be established, this is not the case in civil cases.
Because we have a common law legal system (adversarial), "the judge can only make a decision about what was herd in court and cannot make any other inquiries about the case"1.
"A judge will usually order that the costs of the successful party be paid by the unsuccessful party."1
- Ratio decidendi
- reason for judgement.
- meaning "the reason" or "the rationale for the decision."
- Unlike obiter dicta, the ratio decidendi is, as a general rule, binding on courts of lower jurisdiction—through the doctrine of precedent.
- Obiter dicta
- is a remark or observation made by a judge that, although included in the body of the court's opinion, does not form a necessary part of the court's decision.
- statements constituting obiter dicta are not binding (meaning cannot be used as argument for a precedent), although in some jurisdictions, they can be strongly persuasive.
- The High Court is the final court of appeal in Australia in matters of both State and Federal.
- Must rely on a precedent in a higher court (which implies that the precedents set by the high court are binding in all other courts).
- BUT the Full Court of the High Court is not bound by previous decisions made by the High Court, so the High Court can overrule itself.
- The Full Court of the High Court means all the judges (there are 7 and they are called justices) sit in and vote on the case, rather than just one judge per case.
- The full court of the Federal court means at least three judges sit in.
- Try mostly have an odd number of judges as when making a decision on a case, the majority prevails.
- If you don't like the precedents try to find differences that can distinguish the cases.
- If no precedent, you can look at obiter dicta, or you can look into other jurisdictions (these are not binding but can be persuasive).
Week 7
The Legal Profession
Barristers and Solicitors are distinct parties. They have different roles and have no relation. "Solicitors have more direct contact with the clients, whereas barristers often only become involved in a case once advocacy before a court is needed by the client. Barristers are also engaged by solicitors to provide specialist advice on points of law. Barristers are rarely instructed by clients directly (although this occurs frequently in tax matters). Instead, the client's solicitors will instruct a barrister on behalf of the client when appropriate." (Wikipedia.org, Barrister)
In Australia Barristers are always sole traders. The research for a case is done by the solicitor who gives a brief to the barrister before they appear in the court.
Attorneys are much the same as Solicitors. The term Attorney is used more commonly in the US.
Week 9
Adversarial System
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
- Negotiation
- Informal
- Voluntary
- Both parties meet privately and try to work out a resolution without needing to go to court.
- Can lead to a settlement.
- Private. Unlike adjudication which is public. Companies that don't want the media attention that may come from a court case, make take this option.
- Quick
- Cheaper than adjudication
- One negative for the public is that no precedent is set, so little people cannot rely on large corporations to set the precedents for them.
- Mediation
- Less formal that adjudication.
- Voluntary
- Mediator is present
- Outcome only accepted when both parties agree to it
- Individual may feel in control of the matter rather than their lawyer.
- Business relationships can be maintained
- Conciliation (only for some courts)
- Mandatory
- Mediator present, but cannot enforce/make a decision on the outcome
- Adjudication
-
- Can be lengthy taking from months to years.
- Arbitration
- Tribunals
- Courts
-
- Legislation
- The government changes the law to make a certain dispute clear.
This is very much a scale. At the top the parties very much are in control of the outcome. Whereas at the bottom they don't have much control at all of the outcome (so long as the system is not corrupt). The top is informal, wheras the bottom is formal. At the top things are by agreement, whereas at the bottom things are much by imposition.
Other Legal Institutions
- Tribunals are set up by laws.
- They are like courts but are less formal.
- Unlike courts the strict doctorine of precedent does not apply to tribunals.
The Administrative Decisions Tribunal (ADT) is one such tribunal (they are is the NSW jurisdiction). The Administrative Appeals Tribunal is another tribunal (federal jurisdiction). As per their website "The Administrative Appeals Tribunal (AAT) provides independent review of a wide range of administrative decisions made by the Australian government and some non-government bodies. The AAT aims to provide fair, impartial, high quality and prompt review with as little formality and technicality as possible. Both individuals and government agencies use the services of the AAT."
In most cases if you are unhappy with the tribunals decision you can appeal to a court, although there are conditions on this. For example as stated on the AAT's web site "If you disagree with the Tribunal's decision you may appeal to the Federal Court on a point of law. This means that the Court can only hear an appeal from the Tribunal decision if you or your adviser believe the Tribunal made a mistake in law in deciding your case. Because there are many rules about Federal Court appeals you may wish to get legal assistance."
Week 10
Contracts and Torts
Contracts
- A contract is an agreement that is enforceable through the courts.
- Contracts can be written or verbal, but written contracts are easier to prove.
- For a contract to be valid there must be, (i.e. otherwise the contract is void, meaning its not legally binding)
- An intention by the parties to be legally bound by their promises,
- agreement by the parties on the terms of the contract,
- consideration from both sides.
- If the parties do not intend for a contract to be legally binding and there is agreement on that then the courts will honour this. (See Rose and Frank v Crompton [1923] 2 KB 261).
- When not expressly stated the courts will presume that, (but this can be rebutted, see Wakeling v Ripley (1951) 51 SR (NSW) 183)
- social, family or domestic agreements are not intended to be legally binding, and
- commercial agreements are intended to be legally binding.
Agreement of a Contract
- As mentioned for a contract to be valid it must have agreement by the parties.
- Offer and Acceptance
- An offer is made by one party, and if accepted by the other, then the contract has agreement. (I think that means, if you make an offer they say okay, you cannot go back and not be bound by the contract.)
- An "invitation to treat" is not an offer.
- Lapse of an offer
- Acceptance
- Silence is not acceptance (Felthouse v Bindley (1862) 11 CB (NS) 869) (but an act can be)
- Acceptance must be in response to an offer for the contract to be valid (R v Clarke (1927) 40 CLR 227).
There is a bunch of related conditions regarding selling of goods. See the Trade Practices Act.
Torts
- A tort is a civil wrong.
- Breach of Contract is a tort.
- Don't need to have a contract to commit a tort. eg. Tort of Negligence.
Week 11
Criminal Law
(work in progress)
Criminal Law is meant to cover matters concerning the state.
- There are sanctions for failing to abide by the law. But there is no capital punishment in Australia.
Reasons for sanctions,
- Retribution - "they ought to suffer"
- Deterrent
- Incapacitation - protect society by locking the criminal up in jail.
- Rehabilitation - try to change them so they won't re-offend.
Need,
- proof of crime (actus reus)
- criminal intent (mens rea) (although some "strict liability" crimes don't need this)
Two types of offences,
- Summary offence -> Decided by a magistrate. No jury. Max 2 years imprisonment.
- Indictable offence -> most cases have a jury.
- Prosecution need to prove defendant is guilty beyond a reasonable doubt.
- A hung jury is when the jury cannot come to a unanimous (although now they will accept one who votes different to everyone else) decision.
- A persons previous criminal history can only be made known at the sentencing (after a jury has decided if they are guilty or not).
- The jury decides the defendants guilt/innocence, the judge decides the sentencing.
Sentencing,
- Could be prison.
- Could be periodic or home detention.
- Could be community service.
- Could be a fine.
- Could be discharged on a good behaviour bond.
Week 12
Mabo Decision
Native Title Act 1993 (Cth)
Wik Decision
Native Title (Amendment) Act 1998 (Cth)
References
[1] http://www.fedcourt.gov.au/videos/text_version/how_a_case_travels.html